Hello, We are here today to talk about Defi a bit further with a slight detour. You will find my mining and farming comparison after the BlockFi how-to.
Mining is the lifeblood of proof of work. It validates transactions on the blockchain and miners make coins in the form of a miner fee for these transactions. Without it, Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin would no longer operate.
Yield Farming allows us to lend our coins to Defi Exchanges coins who reinvest them and pay us interest from their profits. As always definitions can be found way below.
How to Yield Farm USDC with BlockFi
Before we begin get a Coinbase and Blockfi account and verify them if you have not already done so. Make sure you use my links so we both get the free BTC boosts.
You should maximize your transfer amounts to save on network fees or deposit it into Coinbase Pro and transfer from there to pay smaller fees.
Mining Vs. Yield Farming
this is my perspective and I know some people are die hard yield farmers or die hard miners. There is some room for both.
Yield Farming Pros:
- You keep your cost basis , so if BTC drops you can simply trade if to BTC for free.
- It doesn’t matter how much BTC or other coins cost when you yield farm it.
The coins are free less taxation. - Coins derived from yield farming are not subject to volatility as they are free. You are really only missing out on the 0.067% you might get from a bank in a savings account if Bitcoin was worthless someday.
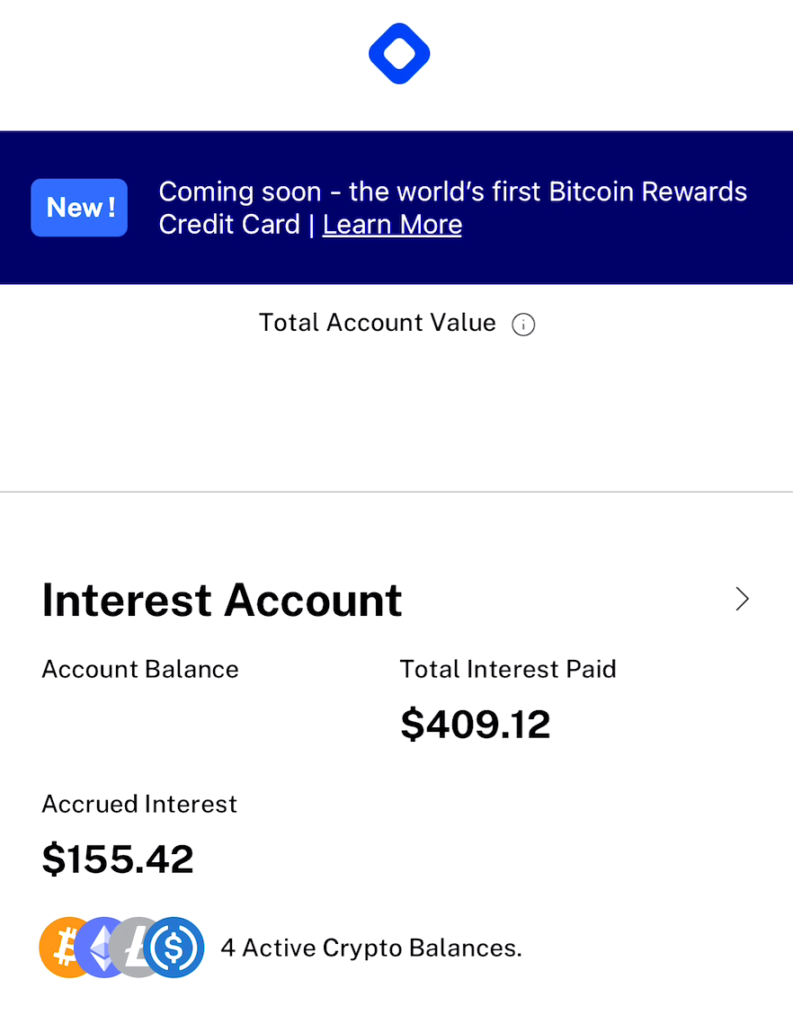
- Bitcoin sometimes appreciates. My yield below was about 1 1/2 months as I zeroed it out. One month was $288 dollars of interest payed in BTC. It is now worth $409.00.
- BTC earns 6% for the first coin then 4% thereafter. So you are getting a multiplier as the free 8.6% coins from USDC are getting 6% (smile).
Yield Farming Cons:
1. It takes more than 10x the amount of USDC at 8.6% to yield profits compared to a powerful mining rig which costs around $4000 for a good multi purpose rig (video editing, gaming etc.). If time is money you might just buy BTC on a dip.
2. It could take you 3-5 days to cash out USDC and convert it to FIAT (USD) in your bank.
3. You have to trust your exchange.
4. One free withdrawal a month or .25 cents plus network fees.
Note: Blockfi payments post on the first business day of the month. However you can see your interest accruing.

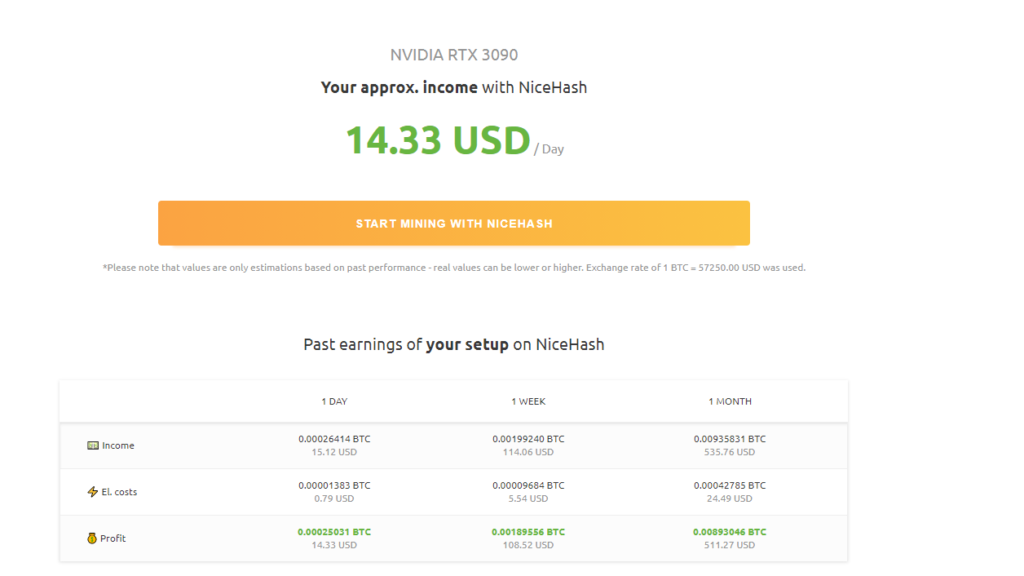
Let’s circle back to mining. A Bad A$$ 4000 dollar off the shelf system (4 year warranty) can generate $500 a month. Lets assume it is mining 1/2 of the time that comes in at $250 a month. You need $40,000 dollars or so at 8.6% to get $288 a month BUT you are out of your cost basis so if BTC dips you are out liquidity to buy BTC . Mining has risks and it can get more difficult or even impossible if BTC drops back to record lows. This happened to me in 2017 and my AASIC miners were door stops metaphorically. It is Pandora’s box 😀
Mining Pros
1. Like farming you get BTC no matter what the price.
2. Unlike an AASIC a PC can be used for gaming, editing, word processing.
Mining Cons
- You spend a cost basis on gear that depreciates.
- GPUs are in short supply when crypto is booming so you have a system or pay a premium for a GPU.
- Systems are loud and heat up.
- Uses a lot of electricity and arguably bad for the environment .
Definitions:
Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is the process of adding transaction records to Bitcoin’s public ledger of past transactions or blockchain. This ledger of past transactions is called the block chain as it is a chain of blocks. The block chain serves to confirm transactions to the rest of the network as having taken place. – bitcoinmining.com
GPU Mining GPU mining is a process of solving complex math problems to verify electronic transactions using computer components – in this case, a graphics card. Miners who participate can either create digital coins or get paid for their processing power in a cryptocurrency. – cryptomintertips
ASIC Mining
ASIC mining is the process of cryptocurrency mining using special equipment. ASICs are created specifically for mining certain coins on the same algorithm. The principles are the same as for a video card: ASICs are engaged in decoding the blockchain and creating new blocks. It differs in that calculations are carried out using special chips. – changelly
Mining Difficulty
Bitcoin mining difficulty determines how difficult it will be to mine the next block and this is why it is referred to as the difficulty of Bitcoin mining. Bitcoin difficulty is a measure of how many hashes (statistically) must be generated to find a valid solution to solve the next Bitcoin block and earn the mining reward. – Coinwarz